By John Patzakis and Charles Meier
Accurate pre-collection data insight is a game-changing capability that enables organizations and their legal teams to determine the scope, volume, and content of electronic information before the very disruptive and expensive step of collecting the data. This insight is enabled through distributed index and search in-place technology.
A true distributed index and search in-place capability for unstructured data requires a software-based indexing technology be deployed directly onto fileservers, laptops, or in the cloud to address Microsoft 365 and other cloud-based data sources. This indexing occurs where the data sources reside without requiring a bulk transfer of the data to a central location. Once indexed, searches can be performed in seconds, supporting complex Boolean operators, metadata filters and regular expressions. Searches can be iterated and refined without limitation, which is critical for large data sets.
While our previous blog post addressed the critical importance of this capability in eDiscovery matters, it is equally essential in information governance projects such as PII audits, the purging of redundant, obsolete or trivial (ROT) data, and due diligence and data separation efforts in support of corporate mergers and acquisitions. Many X1 customers have recently employed our indexing in-place technology on such projects with remarkable success.
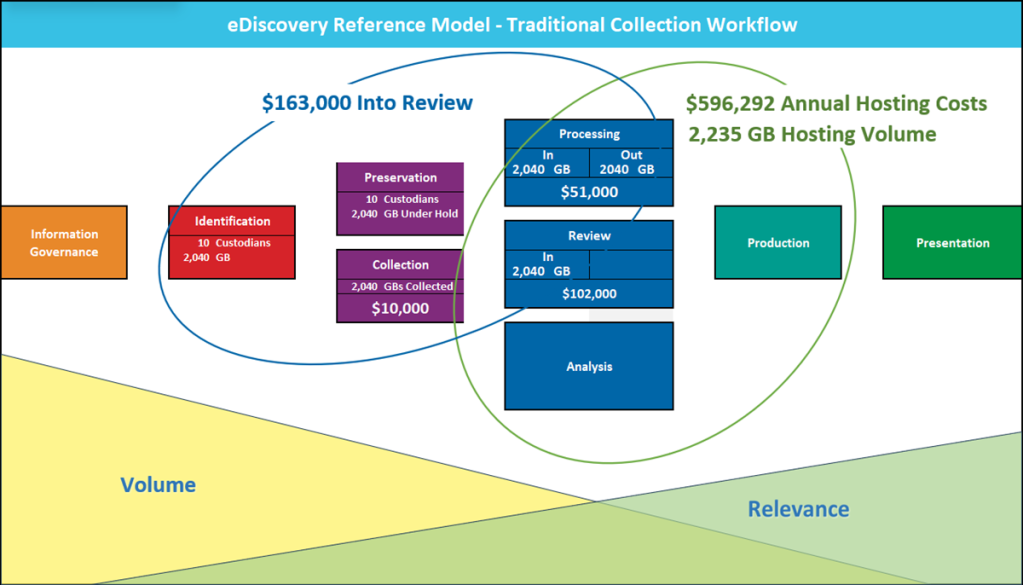
Incredibly, many of these customers also received alternative proposals that leverage traditional eDiscovery workflows presenting much higher estimated costs and much longer durations. Traditional eDiscovery workflows mandate broad and manual data collection, copying and migration efforts, large scale data processing, and loading the data into a different platform for review and analysis. There are three fundamental reasons why this “traditional approach” is fatally flawed for information governance projects.
- Prohibitive Cost and Risk. The data scope of information governance projects involves terabytes and sometimes petabytes of data. Mass collection, copying and migration of these data sets with manual hand-offs for later analysis in a centralized location is extremely expensive, disruptive, and time consuming. Also, mass duplication and egress of enterprise data under control to execute ROT, PII, data separation or other due diligence projects is completely antithetical to their very purpose.
- The “Now What?” Problem. Let’s assume an organization has decided to incur the enormous cost, disruption and risk associated with the mass copying, migration, and centralization of unstructured data, and after loading the data into a review process, a key subset of documents and emails are finally identified for purging or other remedial action. Now what? You are merely working with copies! The live “original” emails and documents are in M365, email accounts, file servers or on laptops. It is possible to manually retrace and remediate, but that process is expensive and disruptive.
- Instant Staleness. Finally, a mass copying and migration effort often requiring several weeks to complete, is immediately stale once eventually completed as the live data in its original location has inevitably changed.
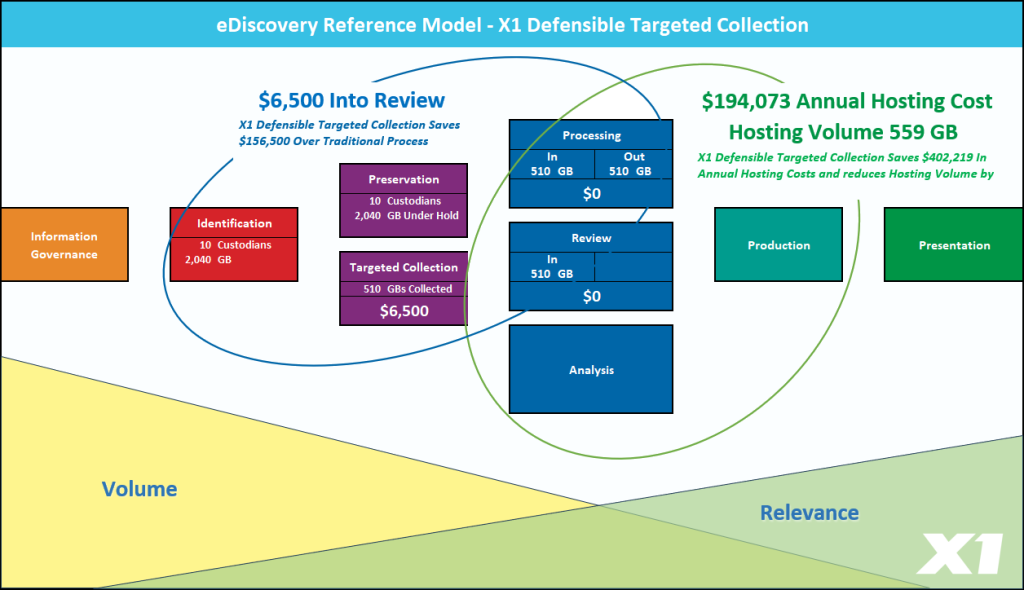
X1 solves these challenges though our proprietary and patented distributed index and search in-place technology that enables scale by bringing true distributed indexing in-place to laptops, file shares, M365 and other cloud sources. X1 Enterprise Collect significantly streamlines information governance workflows by identifying and allowing for the remediation of targeted data in-place, thereby eliminating the need for expensive and cumbersome data duplication and migration.
For a demonstration of the X1 Enterprise Collect Platform, contact us at sales@x1.com. For more details on this innovative solution, please visit www.x1.com/x1-enterprise-collect-platform.